Need want demand & desire –
Key differences explained with examples
Key Points Notes about Customer
needs, wants, and demands
1. Human needs is
the fundamental concept which underlies marketing strategy.
2. Want is the form
human needs take as they are shaped by culture and individual personality.
3. Need is states
of felt deprivation.
4. Demand is human
wants that are backed by buying power.
5. Successful
company is company who successfully learn about and understand its customer
needs, wants, and demands.
6. Customer's need
and want is fulfilled through market offerings.
7. Market offerings
are some combination of products, services, information, and experiences
offered to a market to satisfy a need or a want.
1.
To know the target
customers and target markets
2.
To take strategic
decisions and implementation
3.
To promote the
products with suitable advertisements
4.
To maximize sales
and profits
5.
To know customer’s
willingness to buy the products
6.
To know the number
of customers who are able to buy their products
7.
To know the
influence of demographic, socio-cultural aspects and income levels on the
buying behavior of consumers
8.
To predict sales in
a particular target market
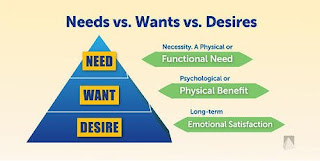
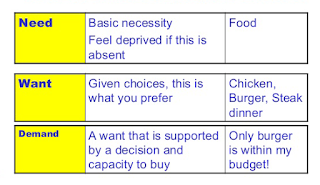
NEED
A need is something that is
necessary for an organism to live a healthy life. Needs are distinguished from
wants. In the case of a need, a deficiency causes a clear adverse outcome: a
dysfunction or death. In other words, a need is something required for a safe,
stable and healthy life (e.g. air, water, food, land, shelter)
Human needs are the basic
requirements and include food clothing and shelter. Without these humans cannot
survive. An extended part of needs today has become education and
healthcare
in todays tough and competitive
world, so many brands have come up with the same offering satisfying the needs
of the customer, that even the “needs category product” has to be pushed in the
customers mind. Example of needs category products / sectors – Agriculture
sector, Real Estate (land always appreciates), FMCG, etc.
Basic needs such as air, water,
food and protection from environmental dangers are necessary for an organism to
live. In addition to basic needs, humans also have needs of a social or
societal nature such as the human need to socialise or belong to a family unit
or group. Needs can be objective and physical, such as the need for food, or
psychical and subjective, such as the need for self-esteem.
Needs and wants are a matter of
interest in, and form a common substrate for, the fields of philosophy, biology,
psychology, social science, economics, marketing and politics.
Classification of Needs
Stated What the customer asks for
Real What the stated needs actually mean
Unstated What the customer also expects but does not ask for
Delight Needs that are not essential but would delight if met
Secret Needs that the customer does not express, often intangible in
nature
So what are the secret needs? They’re
all the things the customer does not express, and often does not even
acknowledge to themselves.
Needs
Needs are basic requirements such
as food, shelter, clothing, water and safety. Human survival is not possible
without fulfilling these needs, here a need show the status of deprivation.
According to marketers point of view, human needs can create repeated sales
irrespective of wants and status.
If the marketer’s products are in
the needs category then it is not required to put extra promotional efforts to
maximize sales and for repeated purchases. Needs forces the customers to buy
the products continuously and repeatedly.
In order to fulfill the basic
requirements, humans sacrifice their wants, fantasies, and dreams also. So
depending on the product category market decides sales and profits. Products
related to the agriculture sector, water, textile and fast moving consumer
goods etc, comes under need category. customers give very less preference to
brands in the case of products related to need category. For example, if a
person feels thirsty then he/she simply buy water and fulfills the need but
they do not give much preference to a particular brand and they do not wait for
longer hours. This is the reason there we can see sales for similar products at
the same place. Hence, so many brands are offering similar products in order to
satisfy the growing customer needs.
Needs are basic requirements, so no
need to put extra efforts to maximize sales.
Competition does not show much
influence on sales.
Customers give primary importance
to buy the need category products. Ex food, clothes
No need to use celebrity
endorsement in order to create sales, if do so, it does not show much
difference in sales because customers buy need category products without
forcing them or influencing them.
The cost of advertisement is very
less.
Customer’s preferences become very
less while purchasing need category products.
Differences in individual income
levels and nations economic conditions do not show much influence in the
consumption and purchase of need category products.
What is WANTS?
Wants are a step ahead of needs and
are largely dependent on the needs of humans themselves.
For example, you need to take a
bath. But i am sure you take baths with the best soaps.
Thus……Wants are not mandatory part
of life and example of wants category products / sectors – Hospitality
industry, Electronics, Consumer Durables etc, FMCG, etc.
Ø
Generally, the products
which fall under the needs category of products do not require a push.
Ø
Instead the customer
buys it themselves
Wants are not basic requirements
and these are not essential for human survival, but there exists a relation
between needs and wants. If a need arises then it stimulates human tastes and
preferences and finally wants arises, because wants are not immediate needs.
Wants are not permanent and can change depending on the time, people and
location. For example, if a person feels thirsty then he/she can drink water to
fulfill the need but the wants force him/her to drink cool drink or fruit
juice.
Wants are not mandatory but
marketers promote the want category products and services in such a way that
these products are a mandatory part of life. In fact, wants are not necessary
for human survival.
Human wants are playing a vital
role in the production of innovative products and products with different
features. Changing tastes and preferences of the customers forces the marketers
to create new products and services
In the case of needs, customers do
not give much preference to the brands, whereas in the case of wants customers
purchase what they want only. These wants are not immediate needs so that
customers can spend the time to select the desired color, flavor and features.
To promote the want category
products marketers need to put extra efforts in order to satisfy the changing
tastes and preferences and wants as well. In the case of want category
products, competitors can grab the sales with their strategic marketing
approaches. Customer wants can give a space to complementary goods and
substitute products also.
Wants Examples
Pizzas, ice creams, juices, branded cloths, fine quality leather footwear, ornaments, and well-furnished house etc.
Why marketers should know about
want category products
1.
Marketers should put
extra efforts in order to satisfy the changing customer wants
2.
Threat of competition
is very high
3.
Customers give
importance to buy specific goods only
4.
Strategic promotional
approaches are necessary to create sales
5.
Cost of advertisement
is high
6.
Customer preferences
are very high while purchasing want category products
7.
Difference in the
income levels show influence in the purchase decisions because customers give
preference to the needs rather than wants
8.
Human wants can create
a scope to different product lines and product mix
9. Marketers can attract target customers by influencing them with different approaches
What is Demands?
Demands is a
step ahead of wants.
When an
individual wants something which i premium, but he also has the ability to buy
i then these wants are converted to demands
The basic
difference between wants and demands is desire. A customer may desire something
but he may not be able to fulfill his desire. Example of demands – Cruises,
BMW’s, 5 star hotels etc.
You might want
a BMW or a Mercedes for a car. You might want to go for a cruise. But can you
actually buy a BMW or go on a cruise? You can provided you have the ability to
buy a BMW or go on a cruise. Thus a step ahead of wants is demands.
When an
individual wants something which is premium, but he also has the ability to buy
it, then these wants are converted to demands
Needs wants and demands are a part
of basic marketing principles. Though they are 3 simple worlds, they hold a
very complex meaning behind them along with a huge differentiation factor. In
fact, A product can be differentiated on the basis of whether it satisfies a
customers needs, wants or demands. Each of them is discussed in detail in this
article
Demands
Willingness to buy and ability to
pay creates demand for a particular product. Human wants can create willingness
and here, buying power can convert these wants into demands. For example, if a
person is willing to buy a gold chain then the buying power or ability to pay
should support his/her willingness, then only it becomes a demand for the gold
chain.
So the marketers should analyze the
market conditions and income levels of the target customers. If the marketers
do not concentrate on economic conditions of the country and per capita income,
then they may not create sales effectively, though their product is highly
qualitative and value created.
Willingness to buy and ability to
pay creates demand, for example, Gold, Diamonds, Luxury cars, Star hotels etc
Know more about demands
1.
The products which can
create demand are premium products and high priced
2.
Customer willingness is
very high towards purchase of these products
3.
Customer’s income
levels decide whether they buy the product or not
4.
A product cannot create
sales effectively when the buying power of the customer is not supported
5.
Ability to buy can
convert the wants into demands
6. Marketers should take production and supply decisions according to the market demand only.
Examples of NEED
The 3 types of needs can be
categorised as follows
1) Existing need
Any need of the customers which is
short term and is easily available is known as existing need. If i need to
prepare food, i need a microwave or other utensils. These are immediately
available in the market and i can purchase them easily. If i need to store
food, i need a refrigerator. If i need to throw away the leftovers, i need a garbage
bin.
Existing need - Types of needs
There are many businesses which
cater to the existing needs of customers. Because it is a widespread market,
the competition in this market is supposed to be huge. Any country you go to,
you will find hundreds of Home appliances being sold as well as 100’s of retail
showrooms. The need based market segment is also one of the most popular market
segment. A business or a start up generally tries to cater to an existing need
of the customer. Demographic and geographic segmentation is most commonly used
to cater to the existing needs of customers.
2) Latent need
A need of a customer which is there
but has not manifested itself because such a product has not been launched.
Companies which tap the latent needs of customers need a lot of innovation and
might go wrong at times. But these are the companies which have fantastic
profitability, because they cater to the needs of the customers which even the
customer does not know he has.
Latent need - Types of Needs
A perfect example of 2 companies
becoming legendary due to the latent needs they catered to are the SONY Walkman
and later on the Apple Ipod. Sony’s walkman made the music lover independent
and he did not have to stick around his cassette or record player anymore. No
one thought they could listen to music on the move, but as soon as Sony
launched a product, everyone loved it. Creating awareness was the only
challenging part for Walkman. Its market acceptance and penetration was
fantastic.
The same was applicable to Apple
Ipod. Everyone loved a walkman but no one wanted to carry cassettes around all
the time. Plus, they were bored of changing sides of the cassettes and
recharging the walkman after every two hours. So when the Ipod was introduced,
people loved it. MP3 player which they could carry anywhere, which was very
small, and could hold 1000 or above songs at times.
There are examples of latent needs
in other places too. The Microwave is a latent need example. What if you could
instantly heat all your food items within seconds. Same goes for the Induction
cooktop, where you can cook food on electricity instead of relying on gas. You
get a cooktop which you can carry with yourself even to remote places as long
as you have electricity there. You can take it for hiking or trekking in your
caravan.
3) Incipient need
It is a type of need which people
want but there is no product to satisfy that need. For example – I want to read
books even when i am sleeping. Or i want to travel all across the world even though
my salary is meager. Till date, there are no products which can satisfy these
needs of customers.
Incipient need - Types of needs
One incipient need which is going
to be satisfied soon is our hopes of going to a different planet. SPACEX
founded by Elon musk is working on this Incipient need itself. SPACEX is
investing in space travel and it is offering a ride to different planets to the
very wealthy customers who want to go to space!! Before SPACEX, only Astronauts
could go to space and many people dreamt of going into space once. So this in
itself can be an excellent example of Incipient need. It’s a need which people
have but this need cannot be satisfied easily. In some cases, it cannot be
satisfied at all.
The most widely known academic
model of needs was proposed by psychologist, Abraham Maslow, in 1943. His
theory proposed that people have a hierarchy of psychological needs, which
range from basic physiological or lower order needs such as food, water and
safety (e.g. shelter) through to the higher order needs such as
self-actualization. People tend to spend most of their resources (time, energy
and finances) attempting to satisfy these basic before the higher order needs
of belonging, esteem and self-actualization become meaningful.[1] Maslow's
approach is a generalised model for understanding human motivations in a wide
variety of contexts, but must be adapted for specific contexts. While
intuitively appealing, Maslow's model has been difficult to operationalize
experimentally





No comments:
Post a Comment